Dynamic Conditional Imitation Learning Autonomous Driving
Hesham M. Eraqi1, Mohamed N. Moustafa2, Jens Honer3
1 Computer Science and Engineering Department, The American University in Cairo, Egypt
2 Last Mile Geospatial team, Amazon, Seattle, Washington, United States
3 Driving Assistance department, Valeo Schalter und Sensoren GmbH, Germany Egypt



Download Paper PDF (Peer-reviewed accepted preprint)
Please cite our work: Hesham M. Eraqi, Mohamed N. Moustafa, Jens Honer. Dynamic Conditional Imitation Learning for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ISSN: 1524-9050, Online ISSN: 1558-0016). Issue 12, Vol 23, Pages 22988-23001. DOI: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3214079, December 2022. [Impact Factor: 9.551]

Paper: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9928072
Code: https://github.com/heshameraqi/Dynamic-CIL-Driving
arXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11579
Video showing D-CIL method in action in test town (better watched in Full-HD):
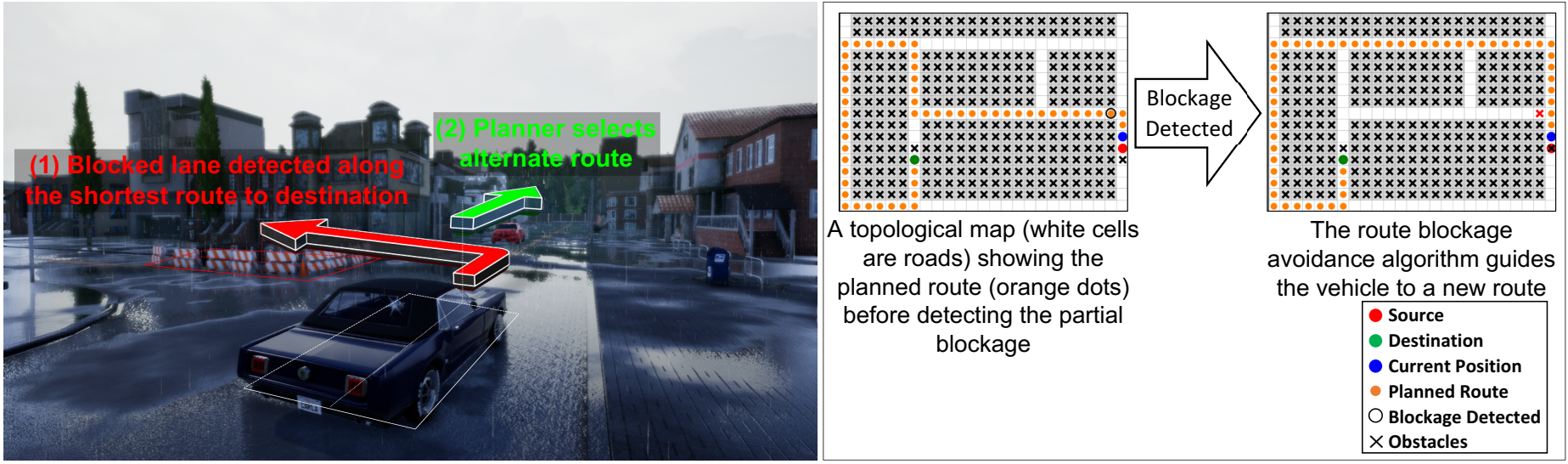
The ego-car successfully detects two road blockages and dynamically estimate and follows new routes to eventually reach the designation successfully.
Summary:
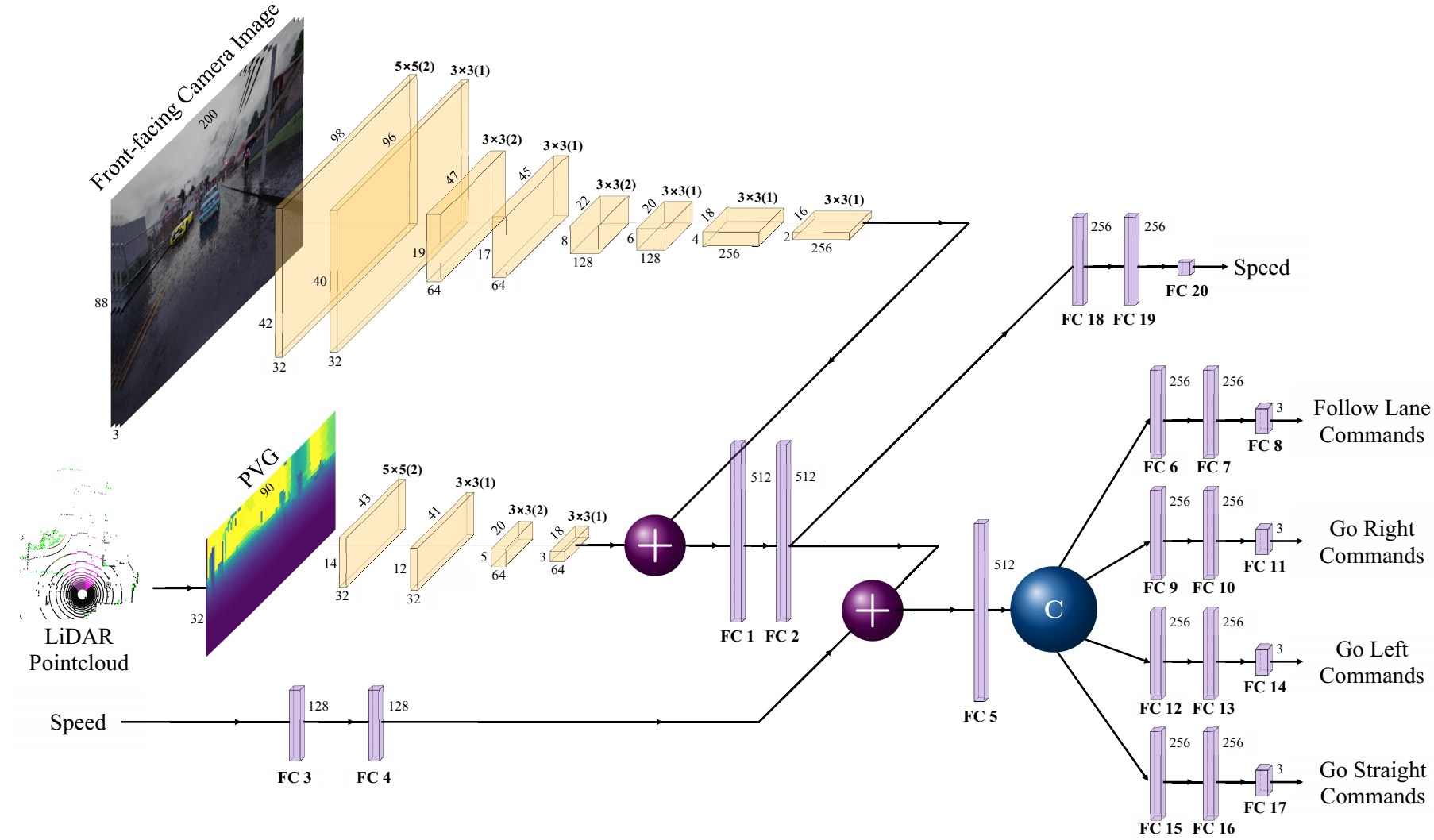
An extension to the Conditional Imitation Learning approach for Autonomous Driving is presented to tackle the challenges of lack of generalization, inconsistency against varying weather conditions, and inability to avoid unexpected static road blockages. The laser scanner input is fused with the regular camera streams, at the features level of the proposed Deep Learning model, to overcome the generalization and consistency challenges. A new efficient Occupancy Grid Mapping method is introduced, with improved runtime performance, memory utilization, and map accuracy, along with new algorithms for road blockages avoidance and global route planning to allow for dynamically detecting partial and full road blockages and guiding the vehicle to another route to reach the destination. Experimental results on CARLA simulator urban driving benchmark demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed methods.